The rapid evolution of technology, including artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain, is transforming the way businesses operate. These innovations bring immense potential but also significant complexity and risk, particularly in auditing and information security management. For IT professionals navigating this new landscape, certifications like Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) and Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) stand out as vital tools for staying ahead.

This article explores how these globally recognized ISACA certifications address the challenges and opportunities presented by AI and blockchain. Whether you're an aspiring auditor or an IT security manager, understanding the relevance of these certifications in the digital age can provide a critical edge in your career.
Understanding CISA and CISM Certifications
Before we discuss their applications in emerging technologies, it’s essential to understand what these certifications entail:
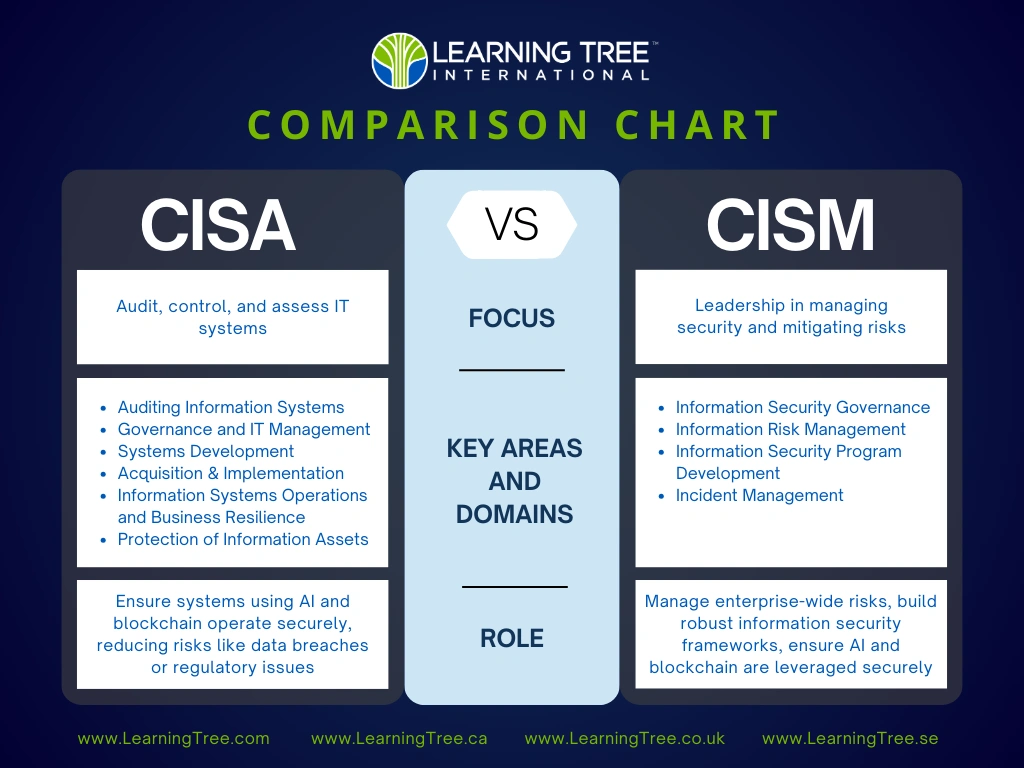
The Key Difference
While both certifications have applications in emerging technology, they serve different purposes. CISA focuses on auditing technology for compliance and performance, while CISM centers on managing enterprise-wide risks and building robust information security frameworks.
Relevance of CISA and CISM in the Age of AI and Blockchain
Emerging technologies like AI and blockchain are transforming industries, but they also bring unique challenges that demand a strategic approach to auditing and security management. Here's how CISA (Certified Information Systems Auditor) and CISM (Certified Information Security Manager) professionals address these complexities:
How CISA Tackles AI and Blockchain
Organizations adopting AI and blockchain need auditors equipped to navigate these technologies' intricate risks and functionalities. CISA-certified professionals play a critical role in safeguarding systems and ensuring operational integrity.
CISA's Role:
- Auditing AI Algorithms and Blockchain Systems:
AI systems depend on sophisticated algorithms that must be accurate, unbiased, and secure to function effectively. Auditors ensure these models perform as intended without compromising data integrity or perpetuating biases. On the blockchain side, its decentralized nature and reliance on smart contracts add another layer of complexity. Auditors evaluate these contracts to confirm they are free of vulnerabilities and verify their performance and integrity, ensuring seamless operations across decentralized networks.
- Regulatory Compliance:
As AI and blockchain adoption grows, governments worldwide are introducing stricter regulations. For instance, AI systems must comply with GDPR for data protection in Europe, while blockchain applications may face transparency and reporting standards. CISA-certified professionals ensure that organizations not only meet these regulatory requirements but also implement best practices to stay ahead of evolving legal landscapes. By doing so, they protect businesses from potential fines and reputational risks associated with non-compliance.
- Risk Identification and Mitigation:
Both AI and blockchain introduce new layers of risk, from cyber threats like data breaches to operational inefficiencies such as inaccurate processing or delays in blockchain transactions. CISA-certified auditors specialize in identifying these vulnerabilities. They conduct thorough risk assessments and develop actionable solutions to enhance system security, performance, and resilience. By addressing these challenges preemptively, businesses can operate more confidently in a competitive digital landscape.
Real-World Example:
A leading multinational financial institution adopted blockchain technology for their settlement system to ensure faster and more secure transaction processing. By engaging CISA-certified professionals, the company was able to conduct an in-depth audit of the system. The auditors uncovered inefficiencies in transaction verification processes and identified potential vulnerabilities within the smart contracts. Through their recommendations, the company enhanced the system's operational resilience and achieved greater efficiency, allowing it to handle a higher transaction volume while maintaining security standards.
In today’s rapidly evolving tech environment, the role of CISA professionals in auditing and securing emerging technologies like AI and blockchain is more crucial than ever. Their expertise ensures organizations can embrace innovation without sacrificing security, compliance, or efficiency.
How CISM Tackles AI and Blockchain Challenges
Emerging technologies like AI and blockchain are transforming industries, but they require more than just routine audits—they need leadership-level decisions to establish and sustain effective security frameworks. The Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) certification equips professionals with the necessary expertise to guide organizations in navigating these challenges effectively.
CISM's Role:
- Developing AI and Blockchain Security Policies:
CISM-certified professionals play a critical role in creating governance frameworks that ensure AI and blockchain technologies align with organizational goals while adhering to stringent security and privacy standards. This includes drafting policies that address risks unique to these technologies, such as data poisoning in AI models or vulnerabilities in smart contracts, ensuring long-term resiliency and compliance.
- Incident Response for AI and Blockchain Systems:
AI-based applications and blockchain networks are increasingly attractive targets for sophisticated cyberattacks due to their growing adoption. CISM holders are skilled at creating robust incident response strategies, enabling organizations to detect and respond to breaches more effectively. From mitigating attacks on an AI model’s decision-making process to managing exploits in blockchain consensus mechanisms, their expertise is key to minimizing damage and maintaining operational continuity.
- Managing Enterprise Security for Disruptive Technologies:
With a proactive approach, CISM-certified leaders oversee the security architecture of enterprise systems, including cloud environments that host AI models and decentralized blockchain platforms. They ensure these cutting-edge technologies are integrated securely into existing operations, addressing risks like unauthorized access to sensitive AI training data or vulnerabilities in blockchain nodes, while safeguarding enterprise assets against evolving threats.
Real-World Example:
When a financial institution implemented AI for real-time fraud detection, the introduction of this disruptive technology presented challenges in both compliance and security. A CISM-certified security leader stepped in, ensuring the system met international data protection laws, such as GDPR, while also preventing vulnerabilities in the machine learning pipeline. Their leadership not only strengthened the system’s integrity but also reassured stakeholders of its reliability and legal compliance.
In a world where technological disruption is constant, CISM professionals are integral for organizations seeking to stay secure while embracing innovation. They don’t just respond to risks—they anticipate and manage them to drive success.
Benefits of CISA and CISM Certifications in Emerging Technologies
Investing in these certifications offers tangible benefits, both for individual professionals and their organizations:

Final Thoughts
The rise of AI and blockchain represents a golden opportunity—and significant challenges—for IT professionals and organizations alike. With ISACA’s CISA and CISM certifications, professionals are equipped to audit and manage these cutting-edge technologies effectively.
Whether you are an aspiring auditor ensuring compliance or a security leader managing enterprise risks, these certifications offer the expertise and credibility to thrive in the digital era.
It’s your move. Take the first step towards career growth by exploring ISACA’s certification programs today!
Further reading: Check out our recent article on this topic: A Day in the Life of a CISA vs. CISM Professional


